Mohit Ratra's Blog
Thursday, November 30, 2017
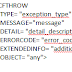
Coldfusion CFTHROW
Sunday, July 9, 2017
Hybris Collections Performance Improvement
lazy.pkcollection.prefetchsize
The default value of this setting is 100. This value controls the number to child entities to fetch when working with one to many relation.
Oracle the max value for this setting is 1000.
Hybris Jalo Session
Hybris Cart Management
Hybris provides the setting to override this behavior. Set the following property to false to change this behavior.
session.remove.cart.on.close=false
Sunday, March 21, 2010
GWT + Spring Security
To understand the problem we should know how spring security handle security exception. In spring we can classify exceptions into authentication exception + authroization exception. To handle spring security exception spring provide exceptiontranslationfilter. When exceptiontranslationfilter catches authentication excetion it uses authenticationentrypoint property and default implementation of authenticationentrypoint redirect user to login page. When exceptiontranslationfilter catches authorization exception it uses accessDeniedHandler property and default implementation of accessDeniedHandler redirect user to access denied page. Spring also provide ConcurrentSessionFilter which stop user from multiple login and if detect multiple login it also redirect to session expired date.
Now above the discussion it is clear that spring filters redirect user in case of exception. But in gwt all rpc call for server are ajax call and if the ajax call triggers security exception we cann't use spring default behavior which redirect user. So how to handle them.
There is one more thing, in gwt all the server call are handled by RemoteServiceServlet and this servlet catches all the exception and serialize them in the gwt serialize format. So exceptiontranslationfilter will not catches any exception.And client will only get status code exception and client code won't be able to display proper message to user.
To solve issue related to RemoteServiceServlet I override its doUnexpectedFailure method and check if the reason of this exception is SpringSecurityException and if it is SpringSecurityException I just throw SpringSecurityException from doUnexpectedFailure method instead to serializing them.
In FilterChainProxy bean I created two filter chains, one to handle RPC calls and one to handle non RPC call. For all the gwt rpc call I wrote custom implementation of concurrentSessionFilter and exceptionTranslationFilter. In the custom implementation of these filter re- throw these exceptions. And to handle all these exception I add one new filter above the springSecurityFilterChain in web.xml and this filter intercepts all gwt rpc calls. This filter catches all the security exception and serializes them.
public class SecurityExceptionWrapperFilter implements Filter
{
private FilterConfig filterConfig;
public void destroy()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException
{
if (req instanceof HttpServletRequest && res instanceof HttpServletResponse)
{
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try
{
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
catch (com.custom.security.exception.SecurityException e)
{
try
{
writeResponse(request, response, serializeException(e));
}
catch (SerializationException ex)
{ RPCServletUtils.writeResponseForUnexpectedFailure(filterConfig.getServletContext(), response, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
RPCServletUtils.writeResponseForUnexpectedFailure(filterConfig.getServletContext(), response, ex);
}
}
}
else
{
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
}
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException
{
this.filterConfig = filterConfig;
}
public String serializeException(Exception e) throws SerializationException
{
final Map
whitelist.put(SecurityException.class, Boolean.TRUE);
whitelist.put(RuntimeException.class, Boolean.TRUE);
whitelist.put(Exception.class, Boolean.TRUE);
whitelist.put(Throwable.class, Boolean.FALSE);
whitelist.put(com.custom.security.exception.SecurityException.class, Boolean.TRUE);
whitelist.put(com.custom.security.exception.AuthenticationException.class, Boolean.TRUE);
whitelist.put(com.custom.security.exception.AuthorizationException.class, Boolean.TRUE);
whitelist.put(com.custom.security.exception.SessionExpiredException.class, Boolean.TRUE);
StandardSerializationPolicy serializationPolicy = new StandardSerializationPolicy(whitelist);
return RPC.encodeResponseForFailure(null, e, serializationPolicy);
}
private void writeResponse(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String responsePayload)
throws IOException
{
boolean gzipEncode = RPCServletUtils.acceptsGzipEncoding(request)
&& shouldCompressResponse(request, response, responsePayload);
RPCServletUtils.writeResponse(filterConfig.getServletContext(), response, responsePayload, gzipEncode);
}
protected boolean shouldCompressResponse(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String responsePayload)
{
return RPCServletUtils.exceedsUncompressedContentLengthLimit(responsePayload);
}
}
Spring Security Overview
To integrate spring security with the enterprise application you need to add one filter to your web.xml
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
DelegatingFilterProxy is a spring class which delegates all intercepted http request to the bean name same as filter name (in this case to the bean name springSecurityFilterChain) configured in the global spring context. Global spring context can be configured by adding the following lines in the web.xml
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:Main-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
The bean with name springSecurityFilterChain can be created automatically by adding the following lines in the spring context file
<http auto-config='true'><intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER" />
</http>
There are few more namespace that you need to add to tell which database provider to use for authentication. These namespace configuration automatically create the required beans.
The other way to use spring authentication is to create all the beans manually. I prefer this way it actually help to customize spring security as per your needs. Example, to create springSecurityFilterChain bean you need to add following line in your context file <b:bean id="filterChainProxy" class="org.springframework.security.util.FilterChainProxy">
<b:property name="filterInvocationDefinitionSource">
<b:value><![CDATA[
CONVERT_URL_TO_LOWERCASE_BEFORE_COMPARISON
PATTERN_TYPE_APACHE_ANT
/login.jsp=#NONE#
/**/*.jsp=concurrentSessionFilter,httpSessionContextIntegrationFilter,logoutFilter,authenticationProcessingFilter,securityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter,exceptionTranslationFilter, filterInvocationInterceptor, securityTransalationFilter
]]></b:value>
</b:property>
</b:bean>
In this way you have you specify all the names of the filter beans from which you want a particular web request need to pass. For all the beans name you specify in this method, you have to create a beans with same using spring bean classes or you can also add your custom bean by extending your bean class with .
Spring security for authentication provide the following filters
- ChannelProcessingFilter
- ConcurrentSessionFilter
- HttpSessionContextIntegrationFilter
- LogoutFilter
- X509PreAuthenticatedProcessigFilter
- AbstractPreAuthenticatedProcessingFilter
- CasProcessingFilter
- AuthenticationProcessingFilter
- BasicProcessingFilter
- SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
- RememberMeProcessingFilter
- AnonymousProcessingFilter
- ExceptionTranslationFilter
- NtlmProcessingFilter
- FilterSecurityInterceptor
- SwitchUserProcessingFilter
Each of these filter have there own task as suggested by there name. Note you need to add them in filter chain in a sequence as suggested by there position attribute.
Coldfusion CFTHROW
Are you using CFThrow to throw custom exception in ColdFusion ? Wait. Read this article before using CFThrow in your application otherwis...

-
Are you using CFThrow to throw custom exception in ColdFusion ? Wait. Read this article before using CFThrow in your application otherwis...
-
Spring security is matured framework for the authentication and GWT is the modern framework to provide a rich internet application. In my ...
-
Spring Security is a Java/Java EE framework that provides advanced authentication, authorization for enterprise application with in few conf...